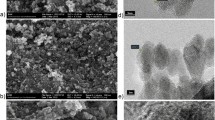
Abstract
The use of magnetic materials as heterogeneous catalysts has attracted increasing attention in the last years since they proved to be promising candidates for water treatment. In the present study, two types of surface-modified magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles, coated with non-hazardous naturally occurring agents—either tannic acid (TA) or dissolved natural organic matter—were evaluated as magnetic heterogeneous catalysts. Chemical synthesis (co-precipitation) was chosen to yield the nanocatalysts due to its well-established simplicity and efficiency. Subsequently, the properties of the final products were fully assessed by various characterization techniques. The catalytic activity in heterogeneous oxidation of aqueous solutions containing a model pollutant, Bisphenol A (BPA), was comparatively studied. The effect of operational parameters (catalyst loading, H2O2 dosage, and UV light irradiation) on the degradation performance of the oxidation process was investigated. The optimum experimental parameters were found to be 1.0 g/L of catalysts and 10 mM H2O2, under UV irradiation. The highest mineralization rates were observed for Fe3O4-TA catalyst. More than 80 % of BPA was removed after 30 min of reaction time under the specified experimental conditions. The obtained results showed that the two catalysts studied here are suitable candidates for the removal of pollutants in wastewaters by means of heterogeneous reaction using a green sustainable treatment method.








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Ai ZH, Gao Z, Zhang L, He W, Yin JJ (2013) Core-Shell structure dependent reactivity of Fe@Fe2O3 nanowires on aerobic degradation of 4-Chlorophenol. Environ Sci Technol 47:5344–5352. doi:10.1021/es4005202
Atacan K, Özacar M (2015) Characterization and immobilization of trypsin on tannic acid modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Coll Surf B 128:227–236. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.01.038
Chong MN, Jin B, Chow CWK, Saint C (2010) Recent developments in photocatalytic water treatment technology: a review. Water Res 44:2997–3027. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2010.02.039
Defoin A, Defoin-Straatmenn R, Hildenbrand K, Bittersmann E, Kreft D, Kühn HJ (1986) A new liquid phase actinometer: quantum yield and photo-CIDNP study of phenylglyoxylic acid in aqueous solution. J. Photochem 33:237–255
Genuino HC, Mazrui N, Seraji MS, Luo Z, Hoag GE (2013) Green synthesis of iron nanomaterials for oxidative catalysis of organic environmental pollutants. Chapter 3. In: New and future developments in catalysis. pp 41–61
Gilmour CR (2012) Water treatment using advanced oxidation processes: application perspectives. Dissertation. University of Western Ontario-Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository. Paper 836
Gorski CA, Handler RM, Beard BL, Pasararnis T, Johnson CM, Scherer MM (2012) Fe atom exchange between aqueous Fe2+ and magnetite. Environ Sci Technol 46:12399–12407. doi:10.1021/es204649a
Hanif S, Shahzad A (2014) Removal of chromium(VI) and dye Alizarin Red S (ARS) using polymer-coated iron oxide (Fe3O4) magnetic nanoparticles by co-precipitation method. J Nanopart Res 16:2429. doi:10.1007/s11051-014-2429-8
Katsumata H, Kawabe S, Kaneco S, Suzuki T, Ohta K (2004) Degradation of Bisphenol A in water by the photo-Fenton reaction. J Photochem Photobiol A 162:297–305. doi:10.1016/S1010-6030(03)00374-5
Liu JF, Zhao ZS, Jiang GB (2008) Coating Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles with humic acid for high efficient removal of heavy metals in water. Environ Sci Technol 42:6949–6954
Munoz M, de Pedro ZM, Casas JA, Rodriguez JJ (2015) Preparation of magnetite-based catalysts and their application in heterogeneous Fenton oxidation—a review. Appl Catal B 176:249–265. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.04.003
Nadejde C, Neamtu M, Hodoroaba VD, Schneider RJ, Paul A, Ababei G, Panne U (2015) Green Fenton-like magnetic nanocatalysts: synthesis, characterization and catalytic application. Appl Catal B 176–177:667–677. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.04.050
Neamtu M, Frimmel FH (2006) Degradation of endocrine disrupting bisphenol A by 254 nm irradiation in different water matrices and effect on yeast cells. Water Res 40:3745–3750. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2006.08.019
Neamtu M, Grandjean D, Sienkiewicz A, Le Faucheur S, Slaveykova V, Velez Colmenares J, Pulgarín C, De Alencastro FL (2014) Degradation of eight relevant micropollutants in different water matrices by neutral photo-Fenton process under UV254 and simulated solar light irradiation—a comparative study. Appl Catal B 158–159:30–37. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.04.001
Nowack B (2008) Pollution prevention and treatment using nanotechnology. Chapter 1. In: Krug H (ed.). Nanotechnology. Volume 2: environmental aspects. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim
Pecher K, Haderlein SB, Schwarzenbach RP (2002) Reduction of polyhalogenated methanes by surface-bound Fe(II) in aqueous suspensions of iron oxides. Environ Sci Technol 36:1734–1741. doi:10.1021/es011191o
Peng L, Qin P, Lei M, Zeng Q, Song H, Yang J, Shao J, Liao B, Gu J (2012) Modifying Fe3O4 nanoparticles with humic acid for removal of Rhodamine B in water. J Haz Mat 209–210:193–198. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.01.011
Qu X, Alvarez PJJ, Li Q (2013) Applications of nanotechnology in water and wastewater treatment. Water Res 47:3931–3946. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2012.09.058
Ren B, Han C, Al Anazi Ah, Nadagouda MN, Dionysiou DD (2013) Iron-based nanomaterials for the treatment of emerging environmental contaminants. Chapter 8. In: Doong R et al. (eds.). Interactions of nanomaterials with emerging environmental contaminants. ACS Symposium Series. American Chemical Society, Washington DC. doi: 10.1021/bk-2013-1150.ch008
Sajiki J, Yonekubo J (2003) Leaching of bisphenol A (BPA) to seawater from polycarbonate plastics and its degradation by reactive species. Chemosphere 51:55–62. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00789-0
Shahwan T, Abu Sirriah S, Nairat M, Boyaci E, Eroglu AE, Scott TB, Hallam KR (2011) Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles and their application as a Fenton-like catalyst for the degradation of aqueous cationic and anionic dyes. Chem Eng J 172:258–266. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2011.05.103
Song XC, Zheng YF, Yin HY (2013) Catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol over Co-doped Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 15:1856. doi:10.1007/s11051-013-1856-2
Sun SP, Lemley AT (2011) p-Nitrophenol degradation by a heterogeneous Fenton-like reaction on nano-magnetite: process optimization, kinetics, and degradation pathways. J Molecular Catal A 349:71–79. doi:10.1016/j.molcata.2011.08.022
Virkutyte J, Varma RS, Jegatheesan V (2010) Treatment of micropollutants in water and wastewater. IWA Publishing, London
Voinov MA, Sosa JO, Pagan S, Morrison E, Smirnova TI, Smirnov AI (2011) Surface-mediated production of hydroxyl radicals as a mechanism of iron oxide nanoparticle biotoxicity. J Am Chem Soc 133:35–41. doi:10.1021/ja104683w
Wang D, Astruc D (2014) Fast-growing field of magnetically recyclable nanocatalysts. Chem Rev 114:6949–6985. doi:10.1021/cr500134h
Wang C, Liu H, Sun Z (2012) Heterogeneous photo-Fenton reaction catalyzed by nanosized iron oxides for water treatment. Int J Photoenergy. doi:10.1155/2012/801694
Zhang J, Zhuang J, Gao L, Zhang Y, Gu N, Feng J, Yang D, Zhu J, Yan X (2008) Decomposing phenol by the hidden talent of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Chemosphere 73:1524–1528. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.05.050
Zhang S, Zhao X, Niu H, Shi Y, Cai Y, Jiang G (2009) Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles as catalysts for the catalytic oxidation of phenolic and aniline compounds. J Haz Mat 167:560–566. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.01.02
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support of the Romanian Ministry of National Education CNCS–UEFISCDI through the national grant PN-II-ID-PCE-2012-4-0477 and BAM Institute (Berlin, Germany). The authors also thank Dr. V. Nica for XRD analysis, Dr. P. Postolache for VSM measurements (Faculty of Physics, ‘Alexandru Ioan Cuza’ University in Iasi, Romania), and Prof. Dr. A. Pui (Faculty of Chemistry, ‘Alexandru Ioan Cuza’ University in Iasi, Romania) for the FTIR recordings.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nadejde, C., Neamtu, M., Hodoroaba, VD. et al. Tannic acid- and natural organic matter-coated magnetite as green Fenton-like catalysts for the removal of water pollutants. J Nanopart Res 17, 476 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-3290-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-3290-0