PROJECT TITLE: Gold nanoparticles-based nanobiocomposites as artificial immunogens for human and animal immunization, respectively, against SARS-CoV-2
PROJECT ACRONYM: Gold-SARS
FOUNDING SOURCE: Romanian Executive Agency for Higher Education, Research, Development, and Innovation (UEFISCDI) - Exploratory Research Projects - PNCDI III - Program 4 - Fundamental and Frontier Research
PROJECT CODE: Project PN-III-P4-PCE-2021-1081
CONTRACT NUMBER: PCE75/2022
PROJECT DURATION: 31 months (02/06.2022 – 31.12.2024)
PROJECT BUDGET: 1.200.000 lei
PROJECT CONSORTIUM: CO - National Institute of Research and Development for Technical Physics, NIRDTP Iasi
PROJECT SUMMARY: The development of anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccines is a current problem of humanity, the preparation of specific immunogens against such types of viruses becoming extremely important for the scientific, economic, technological, social, or cultural domains. Although vaccination is one of the most effective healthcare interventions, there are several social, clinical, and economic obstacles to vaccination, including a large number of people reluctant to new vaccines, the side effects of vaccination, the likelihood of varying vaccine effectiveness or poor efficacy in various populations, longevity of the immune protection and access to the vaccine for certain people.
Gold nanoparticles (AuNP) have aroused huge interest in vaccinology, due to their reliable surface functionalization, biocompatibility, size and shape customization, and optical properties. AuNP were exploited in vaccines against bacterial infections, viral infections, cancer, parasite infections etc.
The goal of the project is to provide the vaccine and nutritional supplements industry with an immunogen against SARS-CoV-2 to be used for COVID-19 prophylaxis. The novelty of the project regards the (a) Immunogen preparation; (b) Applications in vaccinology; (c) Solving the old problem of AuNP stability; (d) Solving the problem of ionic binding stability in aqueous solutions with high ionic strength; (e) Preparation of immunizing nutritional supplements and vaccine industry and (f) Social acceptance.
PROJECT OBJECTIVE: The main objective of the project is to prepare a virus-like immunogen based on gold nanoparticles (AuNP) coated with commercially-available recombinant S (spike) proteins for further use in the development of a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. The resulting vaccine can be used to (1) obtain natural products with immunizing properties (i.e., immunized eggs from vaccinated chickens or lyophilized egg products administered as a nasal spray) that contain anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies to provide passive immunization against coronavirus to those who consume such products of animal origin and (2) for active immunization after direct inoculation of such a vaccine in humans. The solution provided should also function as a common platform for other types of vaccines.
EXPECTED RESULTS:
- A functional anti-SARS-CoV-2 immunogen conditioned as aqueous suspensions of nanometer AuNP-spike bionanocomposites, resembling dimensionally and in surface composition to the coronavirus. Indicator: product
- A method to stabilize the sodium citrate on the surface of gold nanoparticles. Indicator: method
- A functional platform based on citrate-coated gold nanoparticles that can be shared in order to prepare a series of very stable magnetic and non-magnetic gold nanoparticles coated, for instance, with ions of aluminum, iron (as proposed in this project), nickel, cobalt, manganese etc. Indicator: method
- A nature-inspired method to increase the bonding strength between a surface functionalized with carboxyl groups (COO-) and a protein (NH3+ groups). Indicator: method
- A registered international patent, 3 ISI-indexed articles and an article presented to international conference.
Executive summary of the activities carried out during Stage I of the project (2022)
For the period of the first stage, a series of activities were carried out regarding:
(i) development of the study protocol and implementation of the proposed immunogenic design,
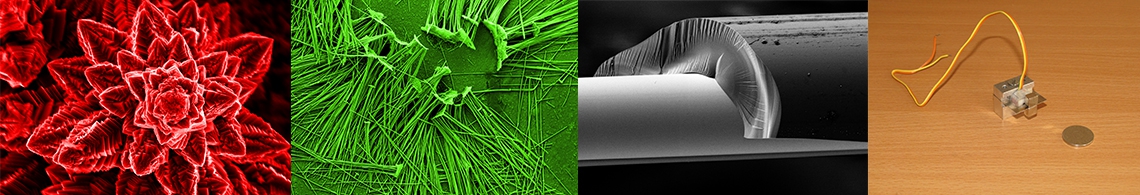
(ii) synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles (NP-Au), coated with sodium citrate, having optimized dimensions,
(iii) preparation and characterization of gold nanoparticles, coated with sodium and aluminum citrate (NP-Au-Al), with sizes comparable to those of SARS-CoV-2, as well as
(iv) in vitro biocompatibility testing on two normal cell types (human fibroblasts and Adipose tissue-Derived Stem Cells (ADSC)) and tumor cells (HeLa cells and human osteosarcoma).
The most significant results concern:
(a) the very high biocompatibility of gold nanoparticles coated with sodium citrate (over 130% in the case of STEM cells),
(b) the obtaining of suspensions of gold nanoparticles functionalized with sodium citrate crosslinked with aluminum ions (NP-Au-Al) with dimensions close to those of SARS-CoV-2,
(c) very good biocompatibility of NP-Au-Al nanoparticles (around 100%)
(d) the obtaining of an excellent stability of gold nanoparticles stabilized with sodium aluminum citrate (NP-Au-Al) in a solution with a very high ionic strength (comparable to that of the blood medium).
(e) significant enhancement of surface plasmon resonance of NP-Au-Al nanoparticles.
Synthesis of gold nanoparticles covered with sodium citrate and aluminum with sizes close to those of SARS-CoV-2, which retain their stability in a solution with a very high ionic strength (NaCl, 4M), along with a significant increase in plasmonic resonance (over 20% compared to NP-Au), is a result of particular importance and significance taking into account that this method, which is most often used to obtain gold nanoparticles and which has its roots in the experiments of M. Faraday in the mid-1850s, being later perfected by Turkevich in 1951, always had this shortcoming of instability in media with medium and high ionic strengths, which limited, to some extent, the use of NP-Au in biomedical applications, including in detection and diagnosis, due to the need of increased amounts of surface-active biomolecules (e.g. enzymes and antibodies) to prevent nanoparticles from agglomeration and destabilization, including in the blood environment.
It was also demonstrated the possibility to introduce aluminum ions into the citrate structure, thus creating the premises for an increased response of the body's immune system, knowing that aluminum is an adjuvant often used in the vaccine industry to stimulate the production of specific antibodies. This approach makes the conventional additional introduction of aluminum-based chemical compounds redundant.
Executive summary of the activities carried out during Stage II of the project (2023)
For the period of the second stage, a series of activities were carried out regarding:
(i) synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles coated with sodium citrate and iron metal ions (AuNP-Fe) to validate the versatility of the method.
(ii) functionalization of AuNP-Al (mainly) and AuNP-Fe (secondary) with commercially available recombinant spike proteins, with final sizes and surfaces comparable to those of SARS-CoV-2.
(iii) registration of an international patent.
(iv) in vitro biocompatibility testing on two normal cell types (human fibroblasts and Adipose tissue-Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs)) and tumor cells (human osteosarcoma and HeLa cells).
The most significant results concern:
(a) excellent biocompatibility of gold nanoparticles coated with sodium citrate and iron ions,
(b) obtaining suspensions of gold nanoparticles functionalized with sodium citrate cross-linked with iron ions (Au-NP-Fe) with dimensions close to those of SARS-CoV-2,
(c) obtaining a good stability of AuNP-Fe in a solution with a very high ionic strength (comparable to that of the blood environment).
(d) significant enhancement of surface plasmon resonance of AuNP-Fe nanoparticles
(e) very good biocompatibility of AuNP-Al and AuNP-Fe nanoparticles functionalized with spike proteins.
(f) a patent for a green method of obtaining cavitary noble metal nanoparticles, mainly gold and silver.
At this stage of the project, the synthesis of gold nanoparticles coated with iron citrate of sizes close to those of SARS-CoV-2 was achieved. The nanoparticles retain their stability in a solution with increased ionic strength (saline), along with a significant increase in plasmonic resonance (more than 116 % higher than in the case of AuNPs). Although the stability is not as high as in the case of cross-linking with aluminum ions, the result is a special one especially through the significant increase of the surface plasmon resonance. Thus, these nanoparticles can be used in biomedical applications, including detection and diagnosis , especially for the useful signal they can provide.
Also, the surfaces of AuNP-Al and AuNP-Fe nanoparticles were successfully functionalized with spike proteins, the resulting compounds being dimensionally close to SARS-CoV-2. Moreover, nanoparticles functionalized with spike proteins were also tested on laboratory animals (the activity being an additional one).
The registered patent concerned cavitary noble metal nanoparticles (without a core), functionalized on the surface with natural molecules, in order to increase their adsorption surface area. The increase of the adsorption surface area is of great interest in the project because it will allow the increase of the loading capacity of nanoparticles with protein spike.
Executive summary of the activities carried out during Stage III of the project (2024)
During the third stage of the project, a series of activities were carried out regarding:
(i) Evaluation of the binding capacity of the immunogen (gold nanoparticles functionalized with commercial recombinant spike proteins) to specific anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, as an indirect indicator of its ability to trigger a specific response from the immune system.
(ii) Development of a general plan by which the immunogen can be tested in an animal model.
(iii) Evaluation of the ability of the immunogen to produce specific anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in laboratory mice after two-dose vaccination.
The most significant results concern:
(a) Optimization of the selection process of gold nanoparticles used as a substrate for AuNP-spike-protein binding to specific anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies.
(b) Demonstration of the binding capacity of AuNP-spike-protein to specific anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies.
(c) Demonstration of the ability of the AuNP-spike-protein immunogen to induce an immune response, in terms of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, in healthy laboratory mice.
(d) Creating the premises of a collaboration between the National Research and Development Institute for Technical Physics - IFT Iași, the company Health Laboratories SRL and the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine in Iaşi for the testing of the immunogen on chickens by the company Health Laboratories for the evaluation of the immune response in order to commercialize immunizing products derived from eggs against SARS-CoV-2, but also for a possible transfer of know-how to the company (which produces and markets immunizing products derived from eggs), under the conditions that INCDFT-IFT Iași holds an invention patent on the method of making the immunogen.
OBTAINED RESULTS:
ISI-indexed articles
- O.-G. Dragos-Pinzaru, G. Buema, D.-D. Herea (autor corespondent), H. Chiriac, N. Lupu, A.E. Minuti, G. Stoian, D. Shore, V.C. Pierre, I. Tabakovic, B.J.H. Stadler, Synthesis and Characterization of Gold-Shell Magnetic Nanowires for Theranostic Applications, Coatings, 12(11):1755 (2022); https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12111755 (IF - 3.236)
- G. Buema, D.-D. Herea, O.-G. Dragos-Pinzaru, Special Issue: Ceramic and Metallic Biomaterials. Application în Medical Sciences, Coatings, 12 (7), 998 (2022); https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12070998 (IF - 3.236)
- Luminita Labusca, Camelia Danceanu, Anca Emanuela Minuti, Dumitru-Daniel Herea (corresponding author) et al. Magnetic nanowires substrate increases adipose-derived mesenchymal cells osteogenesis. Sci Rep, 12, 16698 (2022); https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-21145-z (IF - 4.996)
- Adina-Elena Segneanu, Gabriela Vlase, Teodora Alexandra Lukinich-Gruia, Dumitru-Daniel Herea, and Ioan Grozescu, Untargeted Metabolomic Approach of Curcuma longa to Neurodegenerative Phytocarrier System Based on Silver Nanoparticles, Antioxidants, 11, no. 11: 2261 (2022); https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11112261 (IF - 7.675)
- Herea, D.D.; Zară-Dănceanu, C.-M.; Lăbușcă, L.; Minuti, A.-E.; Stavilă, C.; Ababei, G.; Tibu, M.; Grigoraș, M.; Lostun, M.; Stoian, G.; et al. Enhanced Multimodal Effect of Chemotherapy, Hyperthermia and Magneto-Mechanic Actuation of Silver-Coated Magnetite on Cancer Cells. Coatings 2023, 13 (2), 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13020406 (IF - 3.4)
- Segneanu, A.-E.; Vlase, G.; Vlase, T.; Sicoe, C.A.; Ciocalteu, M.V.; Herea, D.D.; Ghirlea, O.-F.; Grozescu, I.; Nanescu, V. Wild-Grown Romanian Helleborus purpurascens Approach to Novel Chitosan Phyto-Nanocarriers—Metabolite Profile and Antioxidant Properties. Plants 2023, 12 (19), 3479. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12193479 (IF - 4.5)
- Segneanu, A.-E.; Vlase, G.; Chirigiu, L.; Herea, D.D.; Pricop, M.-A.; Saracin, P.-A.; Tanasie, Ș.E. Romanian Wild-Growing Armoracia rusticana L.—Untargeted Low-Molecular Metabolomic Approach to a Potential Antitumoral Phyto-Carrier System Based on Kaolinite. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12061268 (IF - 7)
- Segneanu, A.-E.; Trusca, R.; Cepan, C.; Mihailescu, M.; Muntean, C.; Herea, D.D.; Grozescu, I.; Salifoglou, A. Innovative Low-Cost Composite Nanoadsorbents Based on Eggshell Waste for Nickel Removal from Aqueous Media. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2572. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13182572 (IF - 4.5) - Herea, D.D. and Segneanu, A.-E. contributed equally to this work.
- Zară-Dănceanu, C.M.; Stavilă, C.; Minuti, A.E.; Lăbușcă, L.; Nastasa, V.; Herea, D.-D.; Malancus, R.-N.; Ghercă, D.; Pasca, S.-A.; Chiriac, H.; et al. Magnetic Nanoemulsions for the Intra-Articular Delivery of Ascorbic Acid and Dexamethasone. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11916. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241511916 (IF – 5.3)
- C. Stavilă, D. D. Herea (corresponding author), M. C. Zară, G. Stoian, A.E. Minuti, L. Labușcă, M. Grigoraș, H. Chiriac, N. Lupu, A. Petrovici, A. Aniță, D. Aniță, Enhancement of chemotherapy effects by non-lethal magneto-mechanical actuation of gold-coated magnetic nanoparticles, Nanomedicine-Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine, 60, 2024, 102766, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2024.102766. (IF – 4.2 )
- Buema G, Segneanu A-E, Herea D-D (corresponding author), Grozescu I. Gels for Water Remediation: Current Research and Perspectives. Gels. 2024; 10(9):585. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10090585 (IF – 5.0)
Cumulative impact factor: 49,8
Communications at international conferences/workshops/events
- Dumitru Daniel Herea, Mihaela Camelia Zara, Cristina Stavila, George Stoian, Anca Emanuela Minuti, Luminița Labusca, Marian Grigoras, Horia Chiriac, Nicoleta Lupu, In vitro enhancement of antitumor drug efficacy by magnetic field-assisted rotation of gold-coated magnetic nanoparticles, 10th International Conference on Advanced Materials, ROCAM, 15-18 iulie, 2024, București.
- Anca Emanuela Minuti, Cristina Stavila, Dumitru-Daniel Herea, Horia Chiriac, Nicoleta Lupu, Scanning electron microscopy as pathway to study on the adherence of nanomaterials on cells, 10th International Conference on Advanced Materials, ROCAM, 15-18 iulie, 2024, București.
- Cristina Stavila, Dumitru Daniel Herea, Anca Emanuela Minuti, Camelia-Mihaela Zara Danceanu, Luminița Labusca, Horia Chiriac, Nicoleta Lupu, Silver-coated magnetite for tumor cells treatment, 10th International Conference on Advanced Materials, ROCAM, 15-18 iulie, 2024, București.
- C. Stavila, D. D. Herea, M. C. Zara, G. Stoian, A. E. Minuti, L. Labusca, M. Grigoras, H. Chiriac, N. Lupu, Gold-coated magnetic nanoparticles as enhancers of conventional antitumor drug activity under rotating magnetic fields, Nanomedicine Workshop, “Advancing diagnostic and therapeutic strategies in cancer by means of nanomedicine,” Alexandru Ioan Cuza University of Iași, 5-6 november 2024.
- Dumitru-Daniel Herea, Magnetic and non-magnetic inorganic nanomaterials for biomedical applications, BEHEALTH & DIGITAL 2024 - Hybrid International Event in Healthcare, 22 - 25 October 2024, Cluj-Napoca, Romania (oral presentation).
Book chapter
Dumitru-Daniel Herea, Luminiţa Lăbuşcă, Nicoleta Lupu, Horia Chiriac, Magnetic particles for drug delivery, in Woodhead Publishing Series in Electronic and Optical Materials, Magnetic Sensors and Actuators in Medicine, Editor(s): Horia Chiriac, Nicoleta Lupu, Woodhead Publishing, Elsevier, 2023, Pages 259-304, ISBN 9780128232941, https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-823294-1.00002-6.
Patent applications
- D. D. Herea, N. Lupu, H. Chiriac, G. Stoian, O. G. Dragoș-Pînzaru, G. Buema, C. Stavilă, M. Grigoraș, L. Lăbușcă, C. M. Zară, A. E. Minuti, G. Ababei, D. Gherca
„Metodă ecologică de preparare de nanoparticule cavitare de metal nobil”
Nr. de înregistrarea2023 00290 / 09.06.2023 - D. D. Herea, N. Lupu, H. Chiriac, G. Stoian, O. G. Dragoș-Pînzaru, G. Buema, C. Stavilă, M. Grigoraș, L. Lăbușcă, C. M. Zară, A. E. Minuti, G. Ababei, D. Gherca
Ecological method of preparing cavitary nanoparticles of noble metal”
Patent registration number: PCT/RO2023/000014
The most significant result achieved and the estimated impact of the results achieved
The most significant result of the project was the demonstration of the ability of the proposed immunogen to induce an immune response in laboratory mice, a response translated into the production of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. It was also found that approximately 2.5 months after the injection, the level of platelets increased in all groups of mice injected with immunogen, indicating a risk of blood coagulation, most likely associated with the spike protein. That is why, in order to avoid the appearance of a coagulation phenomenon in humans, we consider the way of their passive immunization to be the most indicated one, by means of immunizing products derived from eggs. Such immunizing products can be made and marketed by a Romanian company. Later, the premises can be created for the use of this immunogen, conditioned in a vaccine, for the immunization of the population. Furthermore, the technology and know-how developed within this project will be able to be used as a versatile platform for obtaining other types of immunogens. Bearing in mind that SARS-CoV-2 infection, even if it has meanwhile become an endemic problem, maintains its active presence in the general population, the tendency being one of chronicity, the placing on the market of some innovative alternatives, whether initially recommended as food supplements with targeted immunizing properties, either as a treatment based on anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies administered in the form of a nasal spray, will represent in the long term a quick, effective and financially accessible solution.
From the point of view of the social impact, the reluctance or even the refusal of a part of the population, at the national and global level, for vaccination is recognized. For this segment of the population, Romanian companies, such as Health Laboratory SRL or ROMVAC, will be able to provide a viable and attractive alternative by putting on the market natural immunizing products against SARS-CoV-2 (passive immunization) produced from immunized eggs from chickens vaccinated with the immunogen made within this project, also offering immunosuppressed patients (transplanted or under biological therapy) or those with autoimmune diseases, who present some risks to vaccination active, the possibility to benefit from an immunization against SARS-CoV-2.
We also estimate that the economic impact of immunization can be significant. Thus, a cost of less than 1 euro per vaccine dose can be estimated. Therefore, taking into account the estimated low costs for the immunogen developed within the project, the economic-financial impact would be extremely positive.
It is necessary to emphasize that the project objective was reached at the end of the project, after the analysis of the data obtained from in vivo testing on laboratory animals. We must also add the fact that we considered it to be of national and institutional interest that the know-how / technology developed within the project be transferred to a Romanian company that would locally produce such products with immunizing properties.
CONTACT DETAILS:
Herea Dumitru-Daniel
National Institute of Research and Development for Technical Physics, NIRDTP Iasi
47 Mangeron Boulevard, 700050, Iasi
email: dherea@phys-iasi.ro
Tel: 0232-430.680
Fax: 0232-231.132